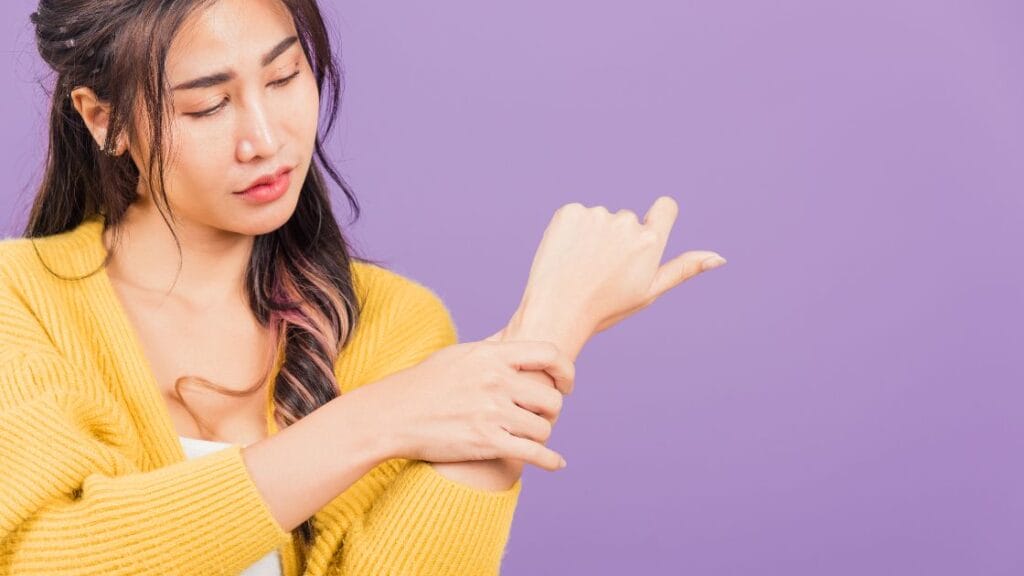
What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway in the wrist that protects the median nerve, which controls sensations to the palm side of the thumb and fingers, except the little finger. Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when this nerve is compressed, leading to numbness, tingling, weakness, or muscle damage in the hand and wrist.
Understanding the Causes and Symptoms
Carpal tunnel syndrome is often caused by a combination of factors, including anatomy, underlying health conditions, and specific patterns of hand use. The common symptoms include numbness, tingling, or a burning sensation in the fingers, especially at night. Pain and weakness in the hand can also occur as the condition progresses.
How Does Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Develop?
Carpal tunnel syndrome can develop due to repeated and forceful motions of the hand and wrist, such as typing or writing, leading to the swelling of the protective tissues surrounding the flexor tendons and median nerve in the carpal tunnel.
Elevate Your Digital Presence
Ready to transform your content strategy? Our expert team delivers SEO-optimized blogs and powerful backlink strategies that drive real results.
Boost Your Content Strategy →Identifying the Risk Factors
There are several risk factors for developing carpal tunnel syndrome, including repetitive movements, wrist position, heredity, and certain health conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and arthritis. These factors can contribute to the compression of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel, leading to the development of the syndrome.
How Does Typing Cause Carpal Tunnel?
Typing and other repetitive hand and wrist movements can contribute to the development of carpal tunnel syndrome. The continuous motion and compression of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel due to typing can lead to numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand and wrist.
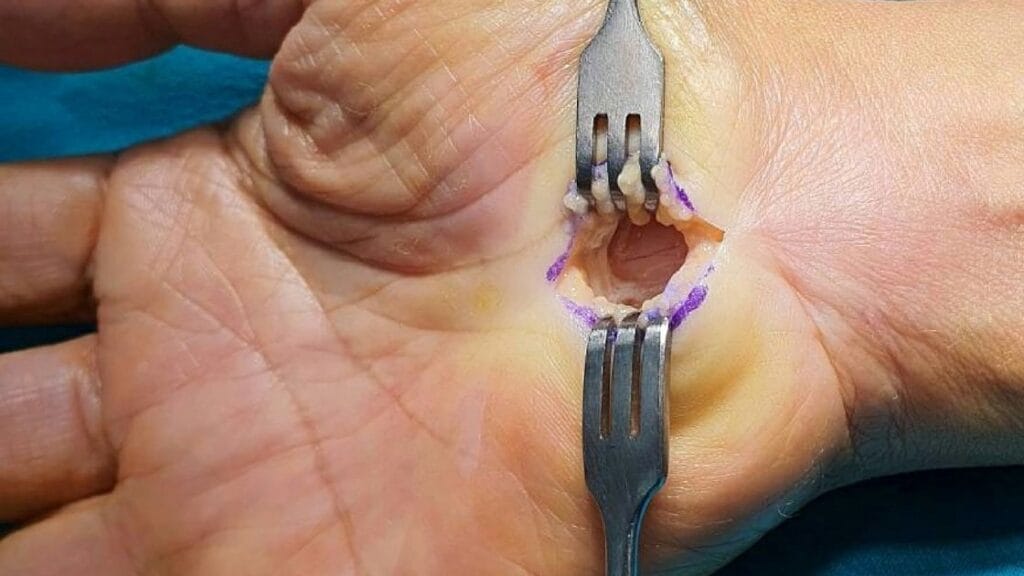
Exploring the Link between Typing and Carpal Tunnel
The repeated flexing and extending motions of the wrist and fingers during typing can cause the tendons in the carpal tunnel to become inflamed, resulting in compression of the median nerve and the subsequent development of carpal tunnel syndrome.
Preventive Measures for Carpal Tunnel due to Typing
To prevent carpal tunnel syndrome from typing, it is essential to maintain proper wrist position, take frequent breaks, and use ergonomic keyboards and wrist supports to reduce the strain on the wrists and hands. Implementing these measures can lower the risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome from typing.
Managing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome from Typing
If carpal tunnel syndrome develops due to typing, various management techniques can be utilized, including physical therapy, wrist splints, and ergonomic adjustments to the workstation. These interventions can help alleviate the symptoms and promote recovery from the syndrome.
Can Writing Lead to Carpal Tunnel?
Similar to typing, repetitive writing can also contribute to the development of carpal tunnel syndrome. The continuous hand and wrist movements involved in writing can lead to the compression of the median nerve, causing numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand and wrist.
Understanding the Impact of Writing on Carpal Tunnel
The repetitive hand and wrist movements while writing can lead to the inflammation and compression of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel, increasing the risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome over time.
Tips for Preventing Carpal Tunnel from Writing
To prevent carpal tunnel syndrome from writing, it is important to maintain good posture, use ergonomic writing tools, and take regular breaks to stretch and rest the hands and wrists. These preventive measures can help reduce the strain on the wrist and minimize the risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome from writing.
Managing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Related to Writing
If carpal tunnel syndrome develops due to writing, treatment options such as wrist braces, corticosteroid injections, and in severe cases, surgery, can be considered to alleviate the symptoms and improve hand and wrist function.
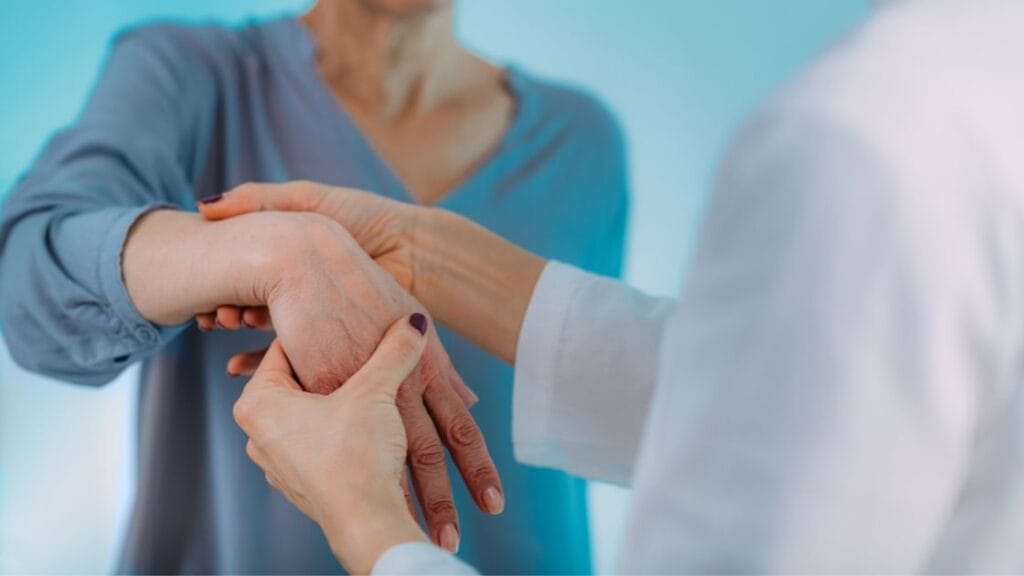

How to Manage Carpal Tunnel Symptoms?
Effective management of carpal tunnel syndrome requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses various treatment options to alleviate the symptoms and promote recovery.
Treatment Options for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Treatment options for carpal tunnel syndrome include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), physical therapy, and corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain and discomfort in the hand and wrist.
Effective Ways to Alleviate Numbness and Tingling
In addition to medical interventions, implementing strategies such as wrist splints, hand exercises, and nerve gliding exercises can help alleviate numbness, tingling, and weakness associated with carpal tunnel syndrome.
Utilizing Wrist Splints for Carpal Tunnel Relief
Wrist splints can provide support and immobilization to the wrist, reducing the pressure on the median nerve and alleviating symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome. Wearing wrist splints, especially at night, can help relieve discomfort and promote better hand and wrist function.
Can Arthritis Cause Carpal Tunnel?
Arthritis, particularly rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, can contribute to the development of carpal tunnel syndrome due to the inflammation and swelling of the wrist joints and surrounding tissues.
Understanding the Relationship between Arthritis and Carpal Tunnel
Arthritis increases the risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome by causing inflammation and compression of the median nerve as a result of the swelling and degeneration of the wrist and hand joints.
Identifying Arthritis as a Risk Factor for Carpal Tunnel
Individuals with arthritis are at a higher risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome due to the underlying joint inflammation and the impact of arthritis-related changes on the structures within the carpal tunnel.
Managing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome in Arthritis Patients
Managing carpal tunnel syndrome in arthritis patients involves a multidisciplinary approach, including medication to address arthritis symptoms, wrist braces to support the affected joints, and, in severe cases, surgery to release the pressure on the median nerve and alleviate carpal tunnel symptoms.

FAQ
What are the causes of carpal tunnel syndrome?
Carpal tunnel syndrome is often caused by repetitive motion, such as typing on a keyboard or using a computer mouse.
How does typing on a keyboard contribute to carpal tunnel syndrome?
Typing on a keyboard involves repetitive wrist motion and can lead to carpal tunnel syndrome due to the strain it puts on the wrist and hand muscles.
What are the treatment options for carpal tunnel syndrome?
Treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome may include wrist splinting, corticosteroid injections, or in severe cases, carpal tunnel release surgery.
Can carpal tunnel syndrome be prevented?
Taking regular breaks during repetitive tasks, using ergonomic keyboards and mice, and practicing proper wrist and hand posture can help prevent carpal tunnel syndrome.
What are the myths surrounding the development of carpal tunnel syndrome?
One common myth is that typing alone can cause carpal tunnel syndrome. In reality, it is a combination of factors including repetitive motion, wrist posture, and individual susceptibility.
How does carpal tunnel syndrome affect the hand and fingers?
Carpal tunnel syndrome causes pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and fingers due to nerve compression in the wrist.
Who is at risk for carpal tunnel syndrome?
Individuals who perform repetitive tasks, have poor wrist posture, or may have a genetic predisposition are at an increased risk for developing carpal tunnel syndrome.
What are some common misconceptions about the development of carpal tunnel syndrome?
Many people believe that only excessive typing can lead to carpal tunnel syndrome, overlooking other factors such as wrist motion, forearm strength, and potential genetic factors.
How can carpal tunnel syndrome be diagnosed?
Diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome may involve a physical examination, nerve conduction tests, and electromyography to assess nerve function and pinpoint the source of symptoms.
What are the surgical options for treating carpal tunnel syndrome?
Carpal tunnel release surgery is a common procedure to treat severe cases of carpal tunnel syndrome, involving the release of the ligament to alleviate pressure on the median nerve in the wrist.
